Linked Lists Concept
Linked Lists Concept
Array vs Linked List
Array
- Static Array needs to double up the array to create more memories (O(N))
- Bad performance when you have to shift indeces over for insert or delete
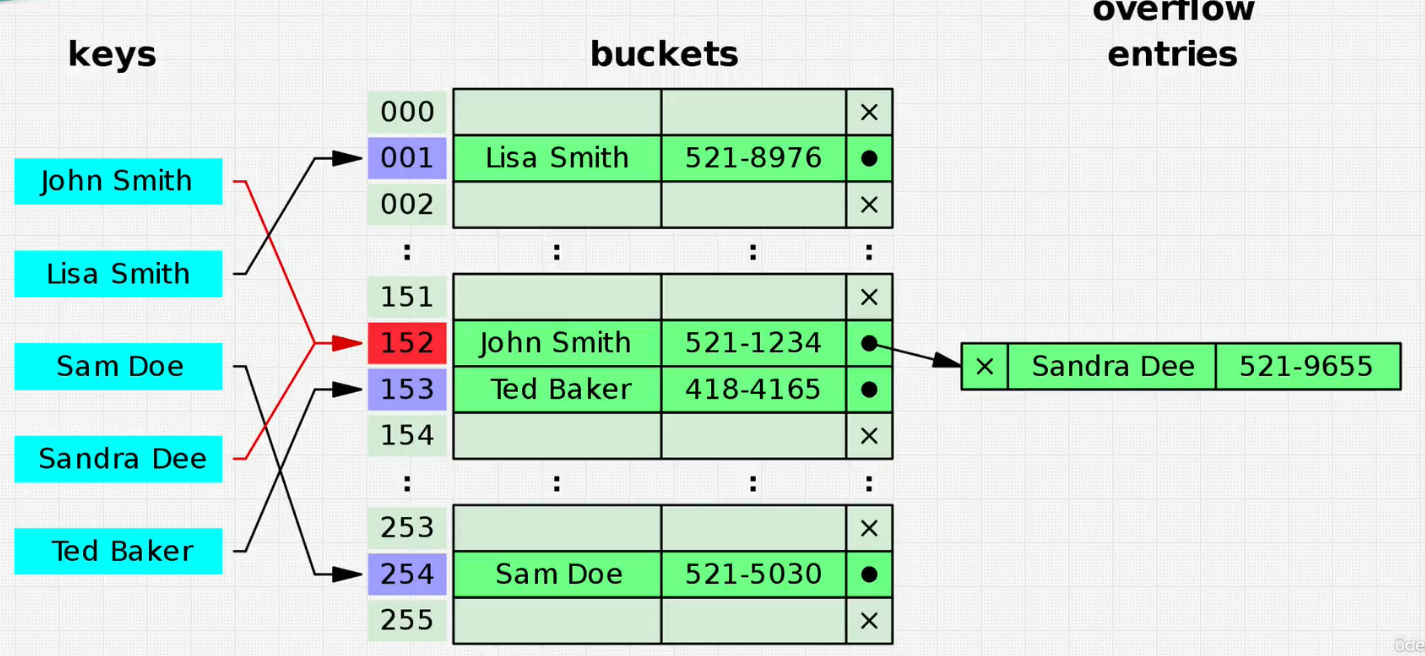
Hash Table
- data structure is not ordered
Linked List

- data is in order
- traversing takes time to read data since memory is scattered
call by reference (change the data inside of object)
let obj1 = {a:true};
let obj2 = obj1;
obj1.a = 'booya';
console.log('1', obj1);
console.log('2', obj2);
call by reference (delete object)
let obj1 = {a:true};
let obj2 = obj1;
delete obj1 //don't delete the object, since obj2 is still referencing obj1.
console.log('1', obj1);
console.log('2', obj2);
let obj1 = {a:true};
obj1 = undefined;
delete obj1 //delete the obj1 data in memory since there is not reference to this data
console.log(obj1)
Linked Lists Kinds
Singly Linked List
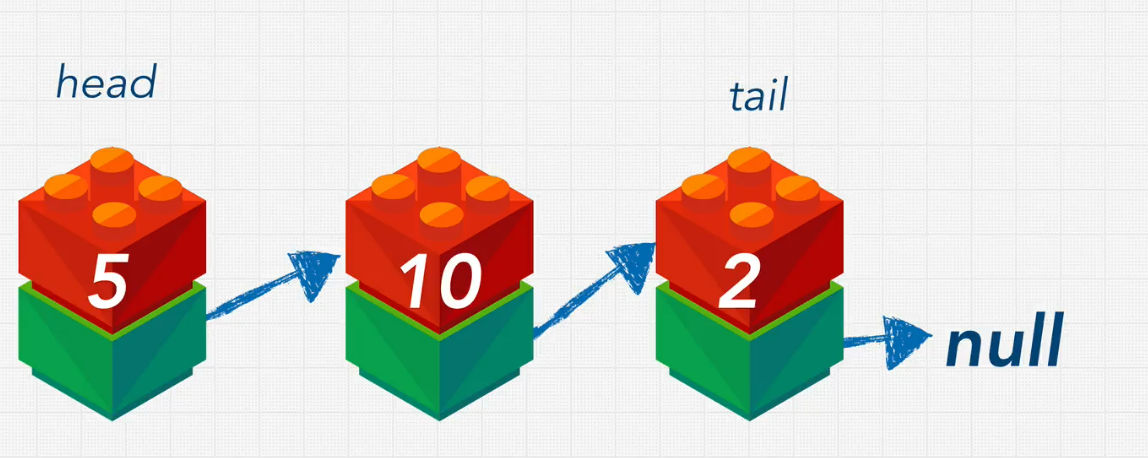

- Simple implementation
- less memory
- delte and insert is a bit faster than doubly linked list
- No way to know the previous node, can't traverse from the back to front
Doubly Linked List
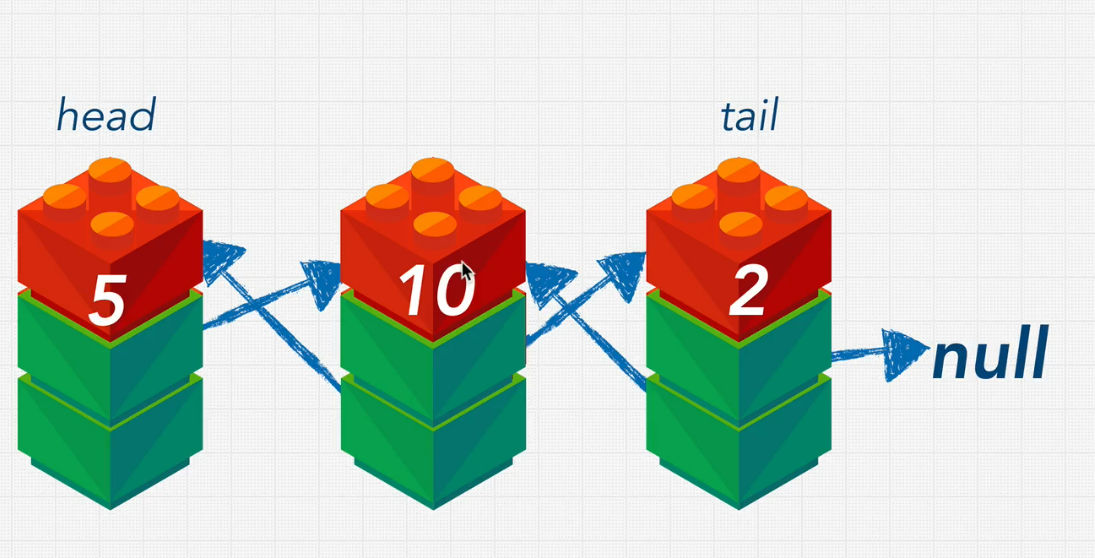
- can traverse from the front and from the back
- requires more memory or storage
- fairly complex to implement
Developing References
Developing Report
2025-01-23 - Linked Lists Concept Report
2025-01-23 - Developing Daily Report
2025-01-4th - Developing Weekly Report
