Hash Tables Concept
Hash Tables Concept
Hash Tables, Object, Maps, Hashes
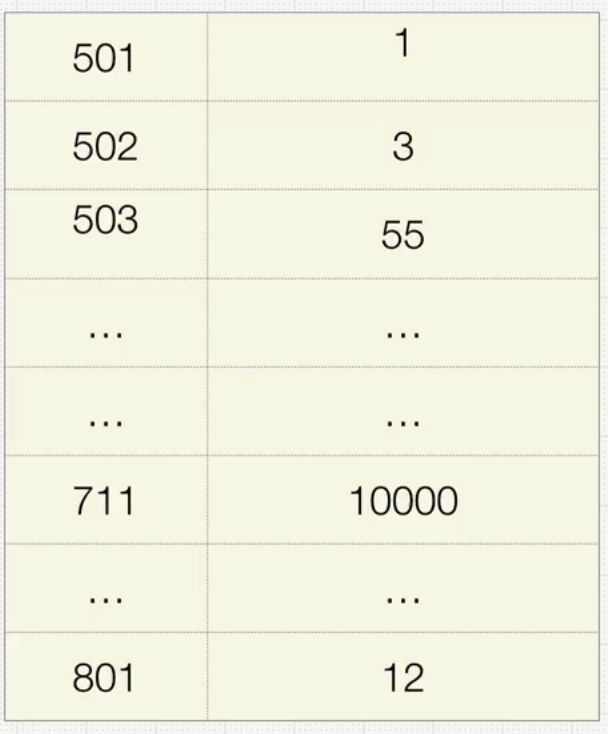
- Key-Value pair
- ex. basket.grapes = 10000;
- Hash Key goes into hash function and return an index where we stored value
- Hash function map key to the memory address where we want to store our values
- Really fast data access. Usually O(1).
- Javascript Object is type of Hash Tables
What is a Hash Function?
- Function that generates a value of fixed length for each input that it gets
- ex. SHA-256, SHA-1
- Idempotent. Hash function is one way. If you give result value to anyone, It isn't possible to know what key was.
- Hash function takes time to process
Hash Tables Functions
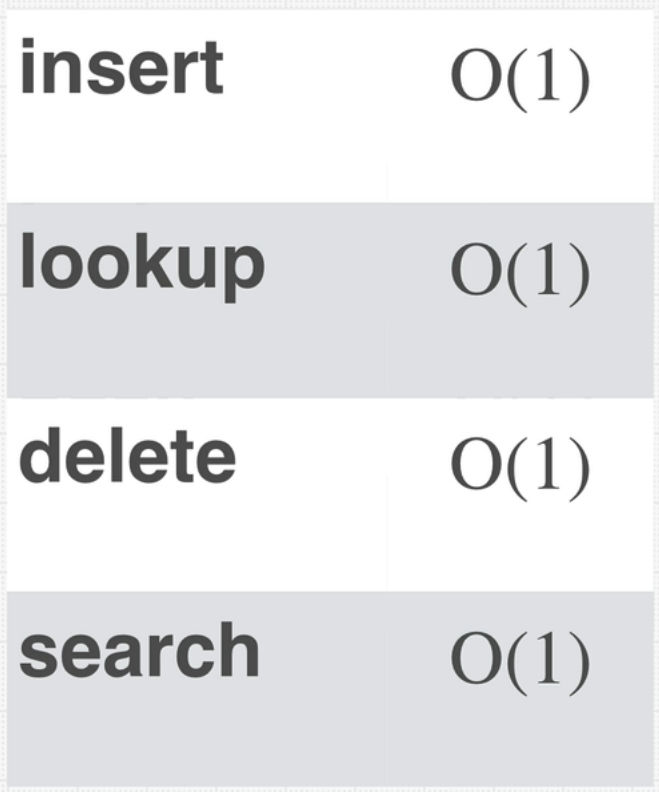
- Insert, lookup, delete, search bigO is all O(1). Because, you have the key assigned everything becomes very simple.
Hash Tables Example
let user = {
age: 54,
name: 'kyle',
magic: true,
scream: function(){
console.log('ahhhhh!');
}
}
console.log(user.age); //lookup O(1)
user.spell = 'abra kadabra'; //Insert O(1)
console.log(user);
user.scream(); //lookup O(1)
Hash Table Problem
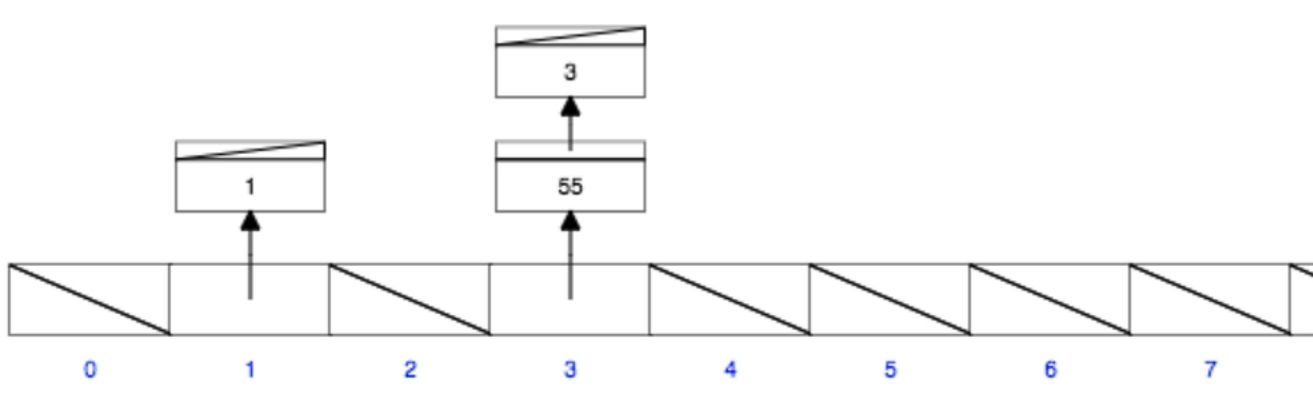
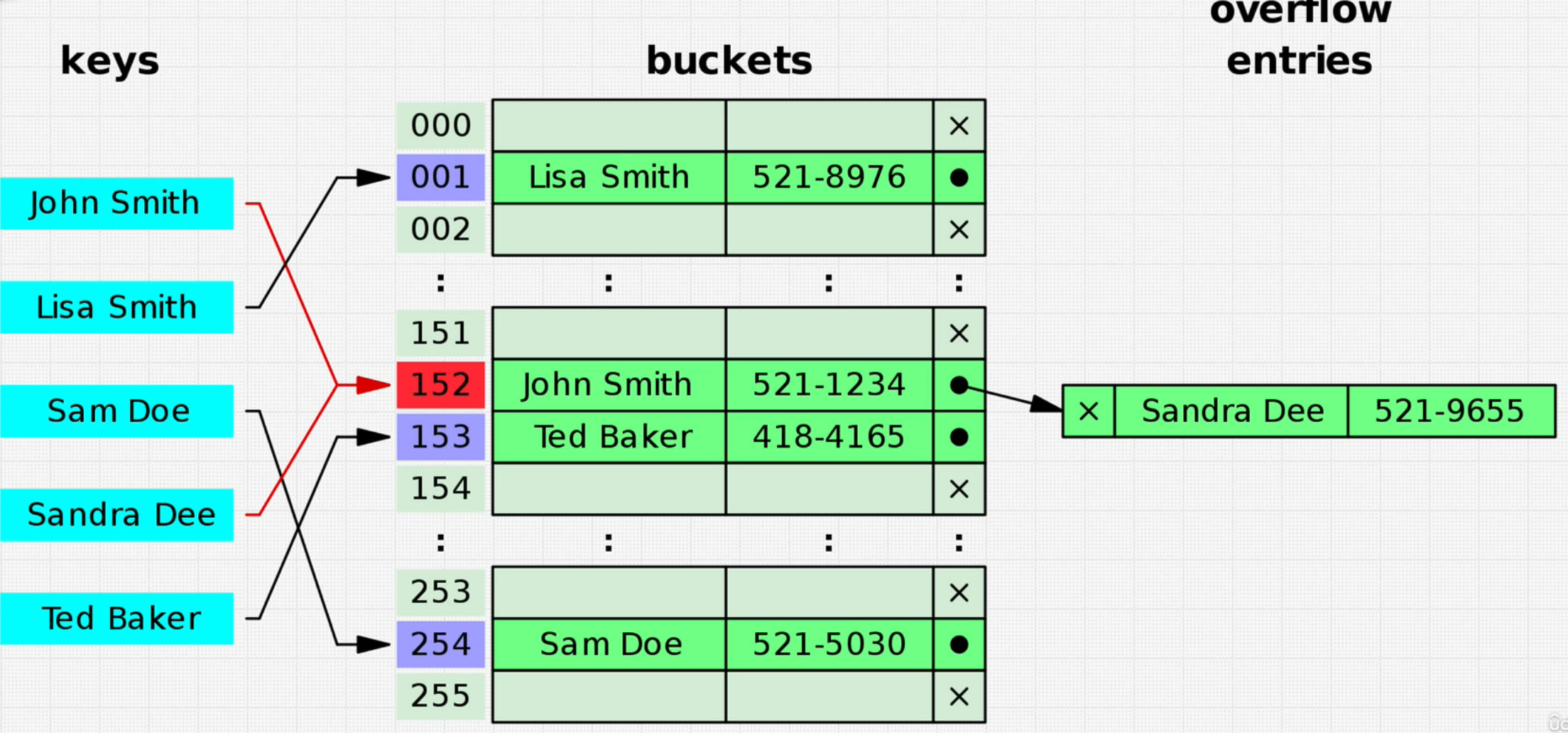
- Collision!
- Hash Function can generate same memory space for different keys, since memory is limited
- When we put different data in the same memory space, we use linked list(separate chaining)
- You will get O(N/K). K = size of the hash table. In worst case scenario, K could be 1, which every data goes into same buckets. Then, bigO will be O(N).
Arrays vs Hash Tables
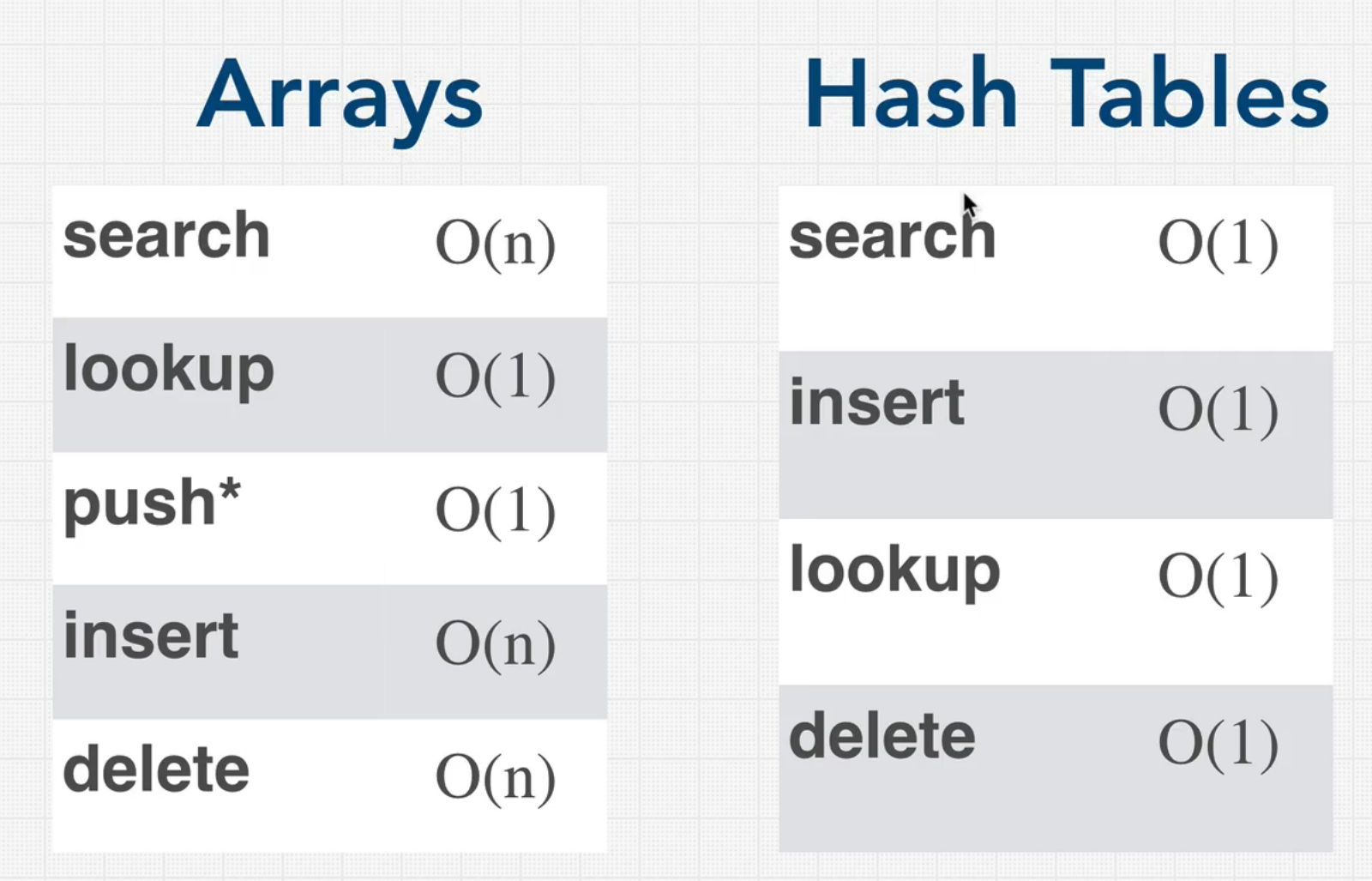
- Hash tables are great for searching, arrays are bad for searching
- keys can be picked in Hash Tables, but array's key is set(index).
- Hash tables data is all over the place, but arrays data will be contiguous
Developing References
Developing Report
2025-01-14 - Hash Tables Concept Report
2025-01-14 - Developing Daily Report
2025-01-3th - Developing Weekly Report
