EC2 Instance Storage
EC2 Instance Storage
EBS(Elastic Block Store)
- Network USB Stick - might be a bit of latency because it is network
- Network drive you can attach to your instances while they run
- Allows your instances to persist data, even after their termination
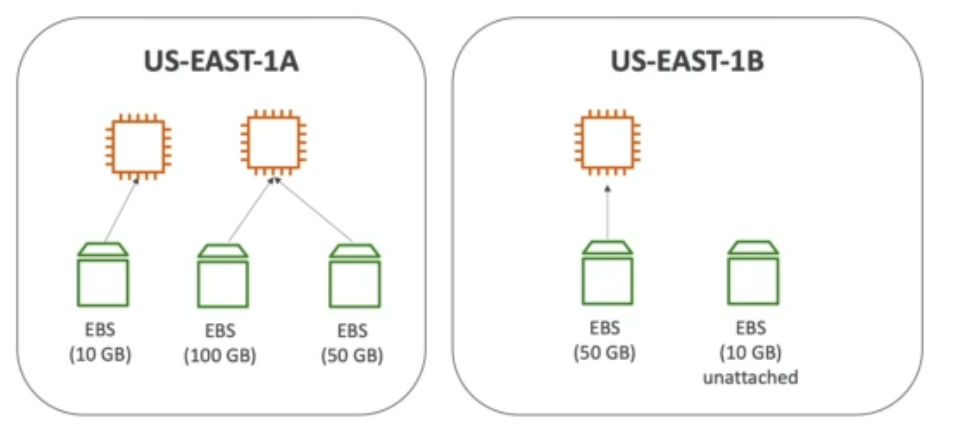
- can only be mounted to one instance at a time (CCP level)
- can be detached from EC2 instance and attached to another one quickly
- Specific Availability Zone
- If you do snapshot, you can move it across zones
- Free Tier : 30 GB of free EBS Storage of type General Purpose (SSD) or Magnetic per month
- Have a provisioned capacity (size in GBs and IOPS)
- Billed for provisioned capacity
- can increase the capacity of the drive over time
- Delete on Termination attribute
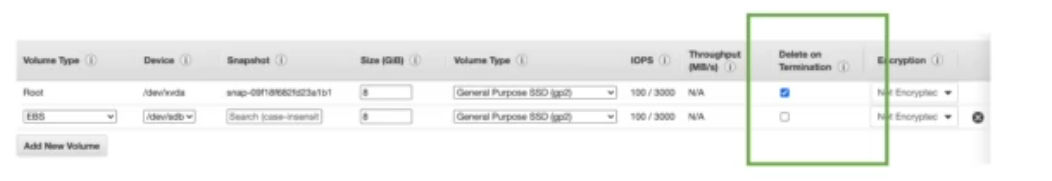
- controls EBS behavior when EC2 terminates
- can be controlled by the AWS console/AWS CLI
- By default, root EBS volume is deleted
- other attached EBS volumes are not deleted
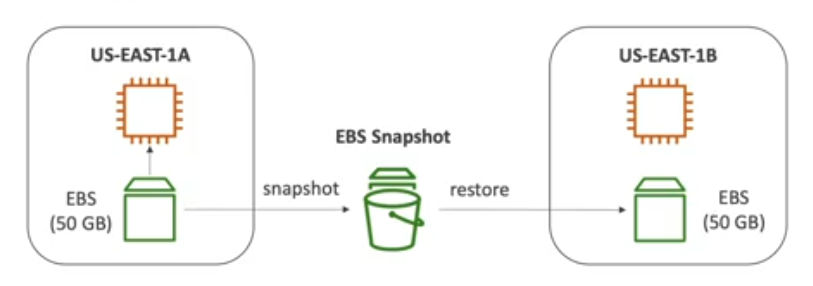
EBS Snapshot
- backup of your EBS volume at a point in time
- Not necessary to detach volume to do snapshot, but recommended
- can copy snapshots across AZ or Region
Features
- EBS Snapshot Archive
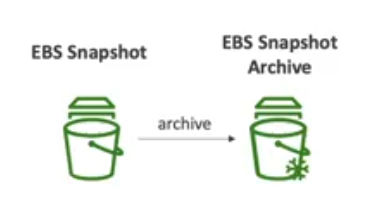
- Move a snapshot to an archive tier that is 75% cheaper
- takes within 24 - 72 hours for restoring the archive
- can change storage tier
- Recycle bin for EBS Snapshots
- retain deleted snapshots so you can recover them from accidental deletion
- Specify retention (1day - 1year)
- Fast Snapshot Restore(FSR)
- force full initialization of snapshot to have no latency on the first use
- when the snapshot is really big or when you need to initialize EBS volume or you need to instantiate very quickly
- costs a lot of money
AMI(Amazon Machine Image)
- what powers EBS instances
- customization of an EC2 instance
- add your own software, configuration, operating system, monitoring...
- faster boot/configuration time because your software is pre-packaged
- built for a specific Region (can be copied across regions)
- Kinds
- Public AMI : AWS provided ex) Amazon Linux 2 AMI
- Your own AMI : make and maintain them yourself
- AWS Marketplace AMI : AMI made by someone else (potentially sells)
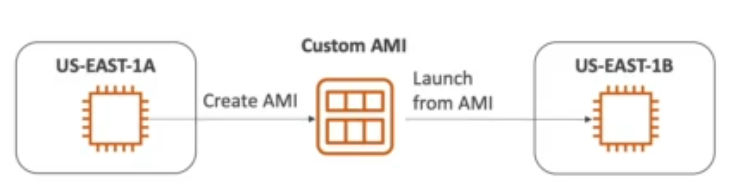
- Process
- Start EC2 instance and customize it
- Stop the instance (for data integrity)
- Build an AMI - also creates EBS snapshots
- Launch instances from other AMIs
EC2 Instance Store
- When you need high-performance hardware disk, use EC2 Instance Store
- EBS - network drives with limited performance
- Better I/O Performance
- EC2 Instance Store lose their storage if they're stopped (ephemeral)
- Good for buffer/cache/scratch data/temporary content
- Not for long term storage
- Risk of data if hardware fails
- Backups and Replication are your responsibility!
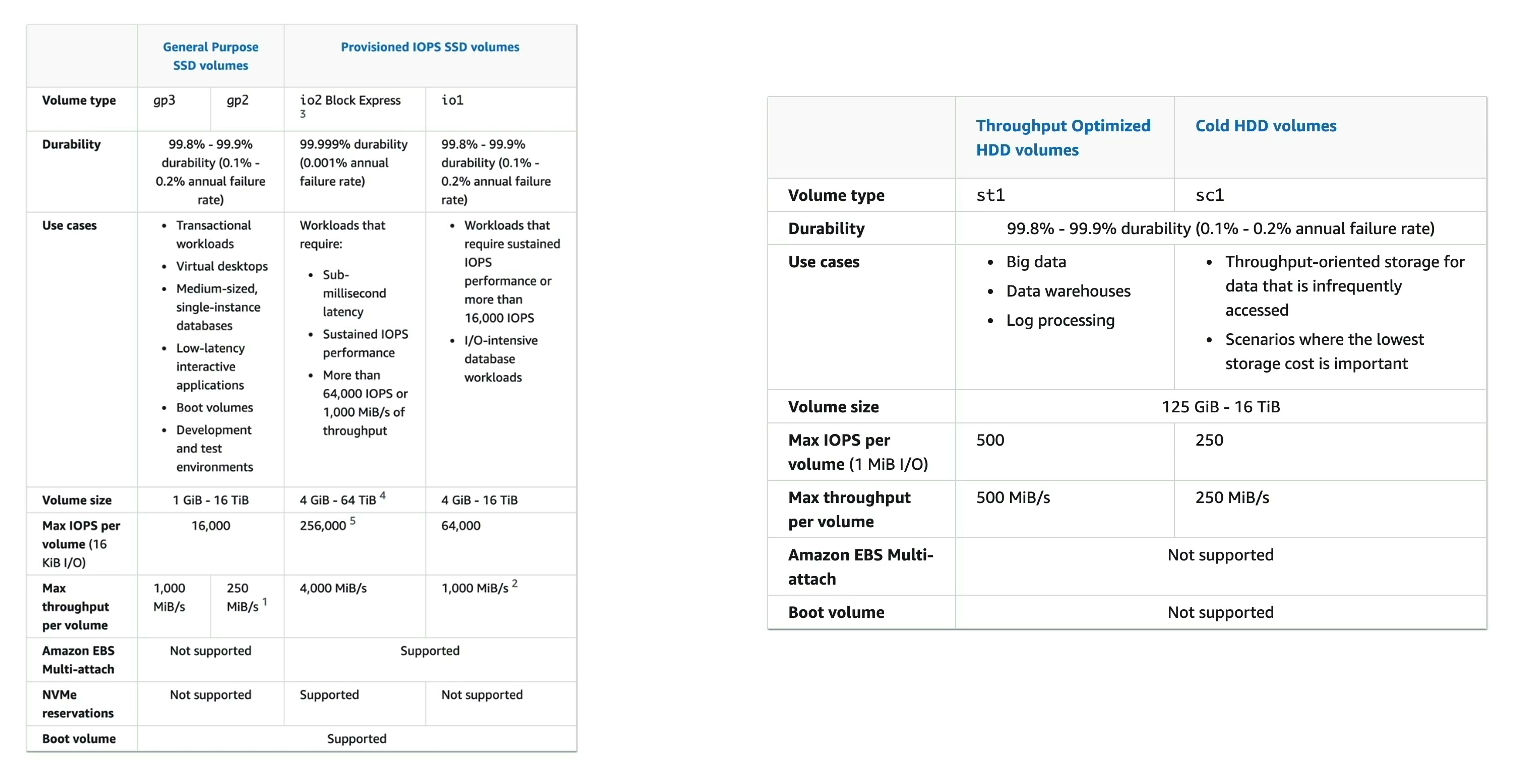
EBS Volume Types
- 6 types
- gp2/gp3 (SSD) : General purpose SSD volume that balances price and performance for a wide variety of workloads
- io1/io2 Block Express (SSD) : Highest performance SSD volume for mission-critical low-latency or high-throughput workloads
- st1 (HDD) : Low cost HDD volume designed for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads
- sc1 (HDD) : Lowest cost HDD volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads
- Size, Throughput, IOPS(I/O Ops Per Sec)
- Only gp2/gp3 and io1/io2 Block Express can be used as boot volumes
General Purpose SSD
- Cost effective storage, low-latency
- System boot volumes, Virtual desktops, Development and test environments
- 1 GB - 16 TiB
- gp3
- baseline of 3000 IOPS and throughput of 125 MiB/s
- can increase IOPS up to 16000 and throughput up to 1000 MiB/s independently (not linked)
- gp2 (older version)
- small gp2 volumes can burst IOPS to 3000
- Size of volume and IOPS are linked, max IOPS is 16000
- if you increase IOPS(number of GBs on your volume), 3 IOPS per GB, means at 5334 GB we are at the max IOPS
Provisioned IOPS(PIOPS) SSD
- Critical business applications with sustained IOPS performance
- applications that need more than 16000 IOPS
- Great for database workloads (sensitive to storage performance and consistency)
- io1 (4 GiB - 16 TiB)
- Max PIOPS: 64000 for Nitro EC2 instances & 32000 for other
- can increase PIOPS independently from storage size
- io2 Block Express (4 GiB - 64 TiB)
- Sub-millisecond latency
- Max PIOPS : 256000 with an IOPS:GiB of 1000:1
- Supports EBS Multi-Attach
Hard Disk Drives HDD
- Can't be a root volume
- 125 GiB - 16 TiB
- st1
- Throughput Optimized HDD
- Big data, data warehouses, log processing
- Max throughput 500 MiB/s - max IOPS 500
- sc1
- Cold HDD
- For data that is infrequently accessed
- Scenarios where lowest cost is important
- Max throughput 250 MiB/s - max IOPS 250
EBS Multi-Attach - io1/io2 family
- Attach the same EBS volume to multiple EC2 instances in the same AZ
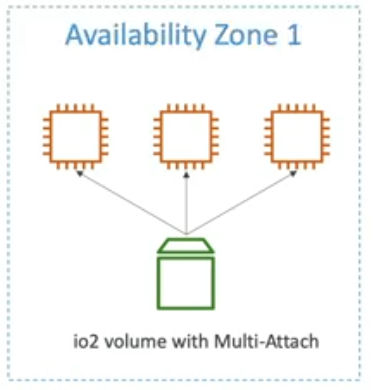
- Each instance has full read & write permissions to the high-performance volume
- Use case
- higher application availability in clustered LInux applications (ex : Teradata)
- Applications must manage concurrent write operations
- Up to 16 EC2 instances at a time
- Must use a file system that's cluster-aware (not XFS, EX4, etc...)
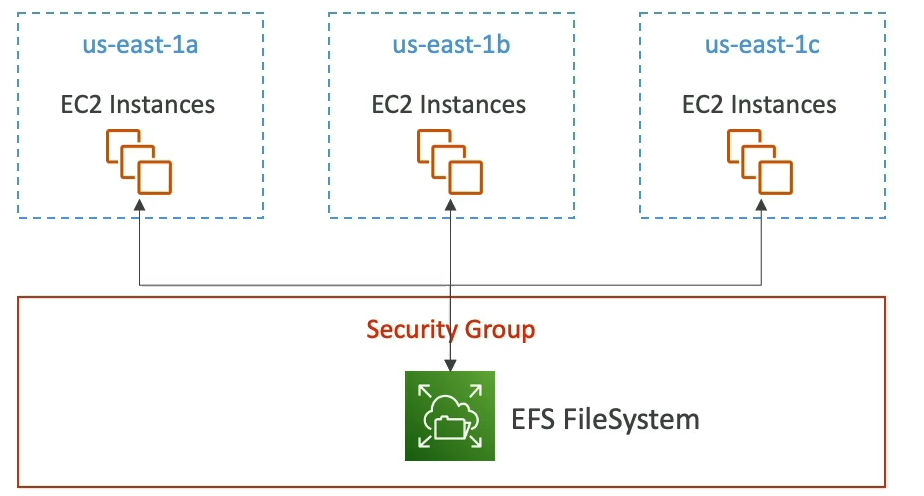
EFS(Elastic File System)
- Managed NFS(Network File System) that can be mounted on many EC2
- EFS works with EC2 instances in multi-AZ
- Highly available, scalable, expensive(3x gp2), pay per use (don't have to pay for capacity provisioned in advance)
- Use case
- content management
- data sharing
- wordpress
- NFSv4.1 protocol
- uses security group to control access to EFS
- Compatible with Linux based AMI (not windows)
- Encryption at rest using KMS
- POSIX file system (~Linux) that has a standard file API
- File system scales automatically, pay-per-use for each GB
Performance & Storage Classes
- EFS Scale
- 1000s of concurrent NFS clients, 10 GB+ /s throughput
- Grow to Petabyte-scale network file system, automatically
- Performance Mode (set at EFS creation time)
- General Purpose (default) - latency-sensitive use cases (web server, CMS, etc...)
- Max I/O - higher latency, throughput, highly parallel (big data, media processing)
- **Throughput Mode
- Bursting - 1TB = 50 MiB/s + burst of up to 100 MiB/s
- Provisioned - set your throughput regardless of storage size, ex:1 GiB/s for 1 TB Storage
- Elastic - automatically scales throughput up or down based on your workloads
- Up to 3 GiB/s for reads and 1 GiB/s for writes
- Used for unpredictable workloads
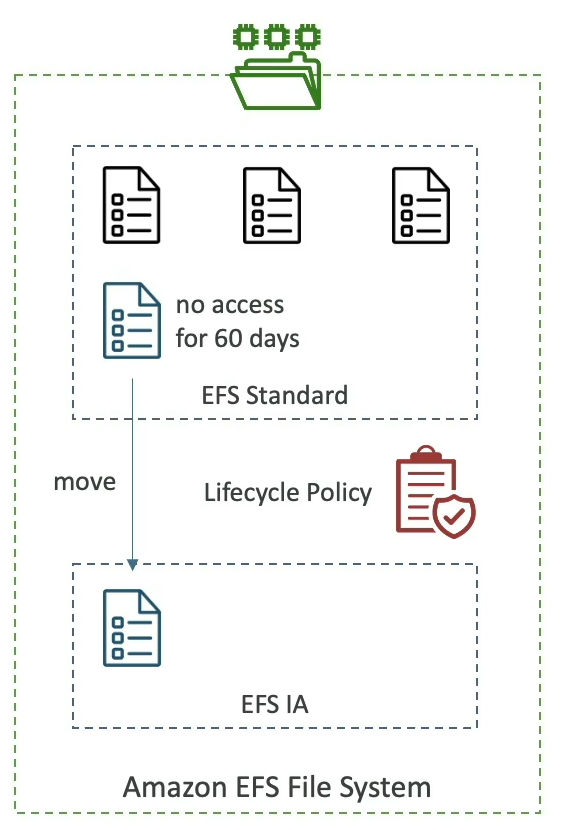
Storage Classes
- Storage Tiers (lifecycle management feature - move file after N days)
- Standard : for frequently accessed files
- Infrequent Access(EFS-IA) : cost to retrieve files, lower price to store
- Archive : rarely accessed data (few times each year), 50% cheaper
- Implement lifecycle policies to move files between storage tiers
- Availability and durability
- Standard : Multi-AZ, great for production, resistant to disaster
- One Zone: One AZ, great for dev, backup enabled by default, compatible with IA(EFS One-Zone IA)
- Over 90% in cost savings
EFS vs EBS
EBS
- EBS Volumes
- One instance at at a time (except multi-attach io1/io2)
- locked at the AZ level
- gp2: IO increase if the disk size increases
- gp3 & io1 : increase IO independently
- To migrate an EBS volume across AZ
- Take a snapshot
- Restore the snapshot to another AZ
- EBS backups use IO and you shouldn't run them while your application is handling a lot of traffic
- Root EBS volumes of instances get terminated by default if the EC2 instance gets terminated
EFS
- Mounting 100s instances across AZ
- EFS share website files (WordPress)
- Only for Linux Instances (POSIX)
- Has a higher price point than EBS
- Can leverage EFS-IA for cost savings
Developing References
Developing Report
2024-11-01 - EC2 Instance Storage Report
2024-11-01 - Developing Daily Report
2024-11-1th - Developing Weekly Report
