Arrays - Question 2 Container With Most Water (Medium)
Arrays - Question 2 Container With Most Water (Medium)
Question
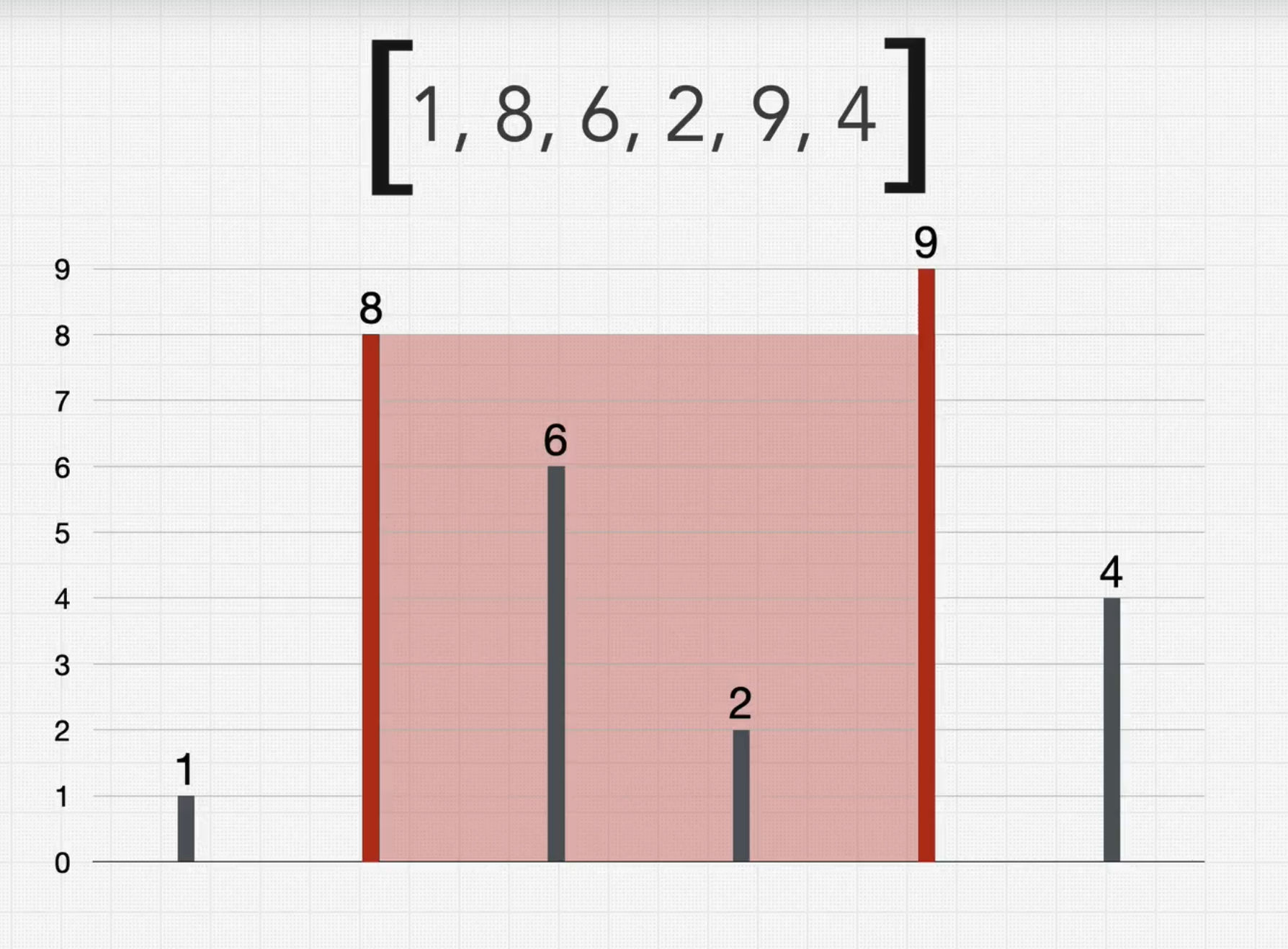
You are given an array of positive integers where each integer represents the height of a vertical line on a chart. Find two lines which together with the x-axis forms a container that would hold the greatest amount of water. Return the area of water it would hold.
Verify the constraints
- Does the thickness of the lines affect the area? If the lines cut into the area in any way that we have to account for when it comes to area calucation - No, assume they take up no space.
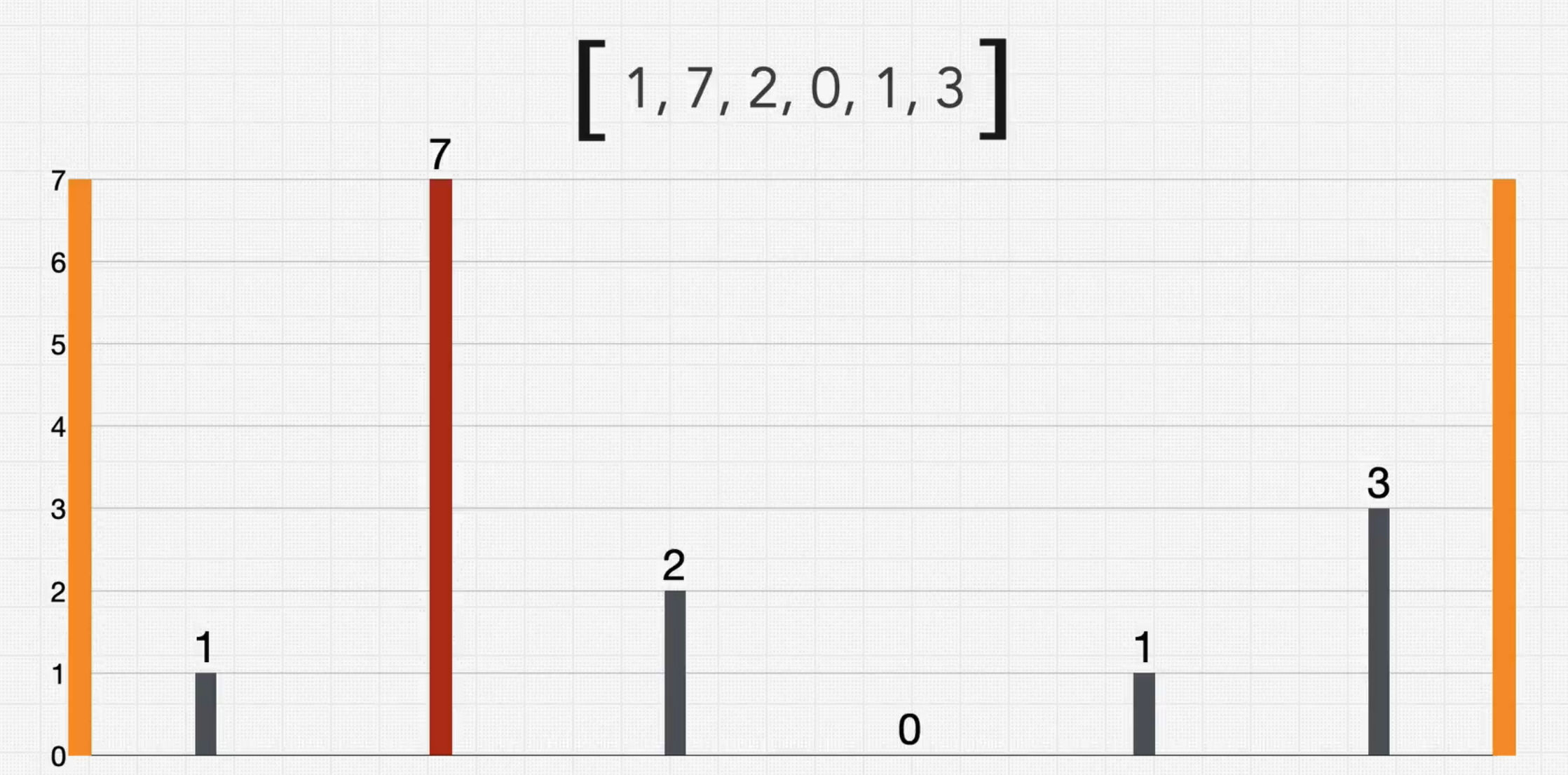
- Do the left and right sides of the graph count as walls? - No, sides cannot be used to form a container. You can't use the side walls such as orange lines below.
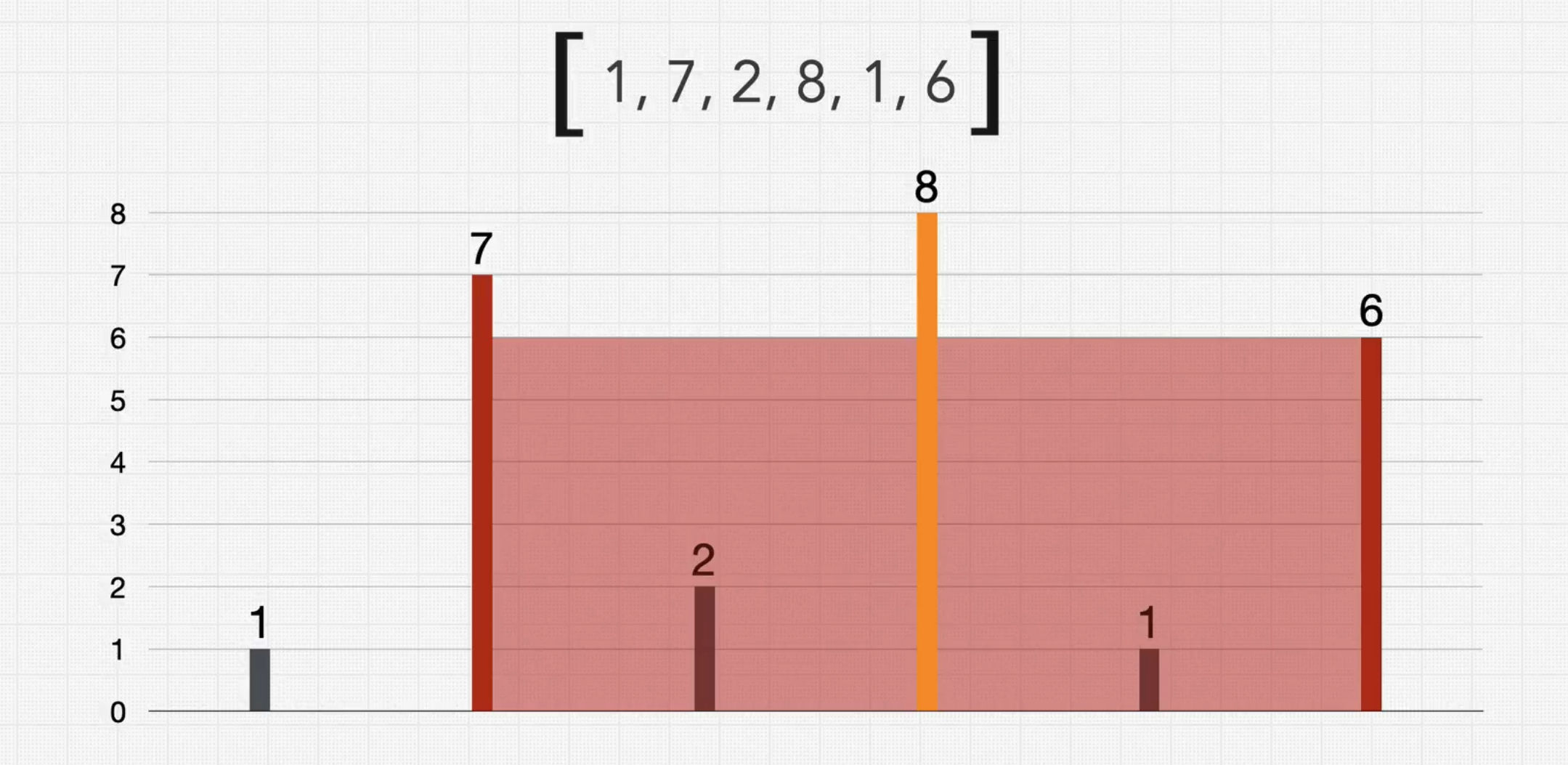
- Does a higher line insde our container affect our area? - No, lines inside a container don't affect the area, meaning the middle line 8 below the graph doesn't affect the container
Write out some test cases
- [7,1,2,3,9] 7, 9 - height 7 x width 4 = 28
- [] 0
- array [1] 0
- [6,9,3,4,5,8] 6, 8 - height 6 x width 5 = 30 / height 8 x width 4 = 32
Figure out a solution without code
- the gap between the indeces should be max, the second highest bar height should be max
- gap fixed => height change - solution 1
- height fixed => gap change
Write out our solution in code
1
function findGreatestAmountOfWater(array){
let width = array.length - 1;
let greatestAmountOfWater = 0;
while(width >= 1){
for(let i = 0; i < array.length && (i+width) < array.length; i++){
let calculatedWater = array[i] * width;
if(array[i] > array[i+width]){
calculatedWater = array[i+width] * width;
}
if(calculatedWater > greatestAmountOfWater){
greatestAmountOfWater = calculatedWater;
}
}
width--;
}
return greatestAmountOfWater;
}
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([6,9,3,4,5,8]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([7,1,2,3,9]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([8]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([1,2,4,3]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([8,7,2,1]));
- Time Complexity: O(N^2)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
2
function findGreatestAmountOfWater(heights){
let maxArea = 0;
let p2 = heights.length - 1;
for(let p1 = 0; p1 < heights.length && p1 <= p2; ){
const height = Math.min(heights[p1], heights[p2]);
const width = p2 - p1;
const area = width * height;
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);
if(heights[p1] < heights[p2]){
p1++;
}else{
p2--;
}
}
return maxArea;
}
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([6,9,3,4,5,8]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([7,1,2,3,9]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([8]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([1,2,4,3]));
console.log(findGreatestAmountOfWater([8,7,2,1]));
- Time Complexity: O(N)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
- Explanation
- p1 starts from index 0
- p2 starts from last index
- Area starts from max width. Area = Math.min(height1, height2) x width, so for now we don't care about width, since width is going to be decreasing from now on. We care about height factor. The way we could increase height as much as possible is if we decrease the area's width by choosing the indicator(p1 or p2) that has smaller value and move it to next index.
- ex. [6,9,3,4,5,8] => p1 = 6, p2 = 8. initial width = 5. 4 cases for moving indicator
- p1 move to index 1. if height value for index 1 is bigger than height value for index 0. (6 -> 9)
- width = 4 (decreased) height = 8 (increased) (9 > 8) => can be increased
- p1 move to index 1. if height value for index 1 is smaller than height value for index 0. (ex. 6 -> 3)
- width = 4 (decreased) height = 3 (decreased) (3 < 8) => decreased
- p2 move to index 4. if height value for index 4 is bigger than height value for index 5. (ex. 8 -> 9)
- width = 4 (decreased) height = 6 (no change) (6 < 9) => decreased
- p2 move to index 4. if height value for index 4 is smaller than height value for index 5. (8 -> 5)
- width = 4 (decreased) height = 5 (decreased) (6 > 5) => decreased
- Only possibility that the whole area can be increased is when we move indicator that has smaller height value in previous comparison to the next position.
- p1 move to index 1. if height value for index 1 is bigger than height value for index 0. (6 -> 9)
- ex. [6,9,3,4,5,8] => p1 = 6, p2 = 8. initial width = 5. 4 cases for moving indicator
Double check for errors
Test our code with our test cases
Analyze Space and Time Complexity
- Solution 1 has bad time complexity. O(N^2) Space complexity is O(1).
- Solution 2 is the best, since it has good time complexity O(N) compared to the first one and good space comlexity as well! O(1)
Developing References
Developing Report
2025-01-14 - Arrays - Question 2 Container With Most Water (Medium) Report
2025-01-14 - Developing Daily Report
2025-01-3th - Developing Weekly Report
