AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Professional
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Professional
CICD
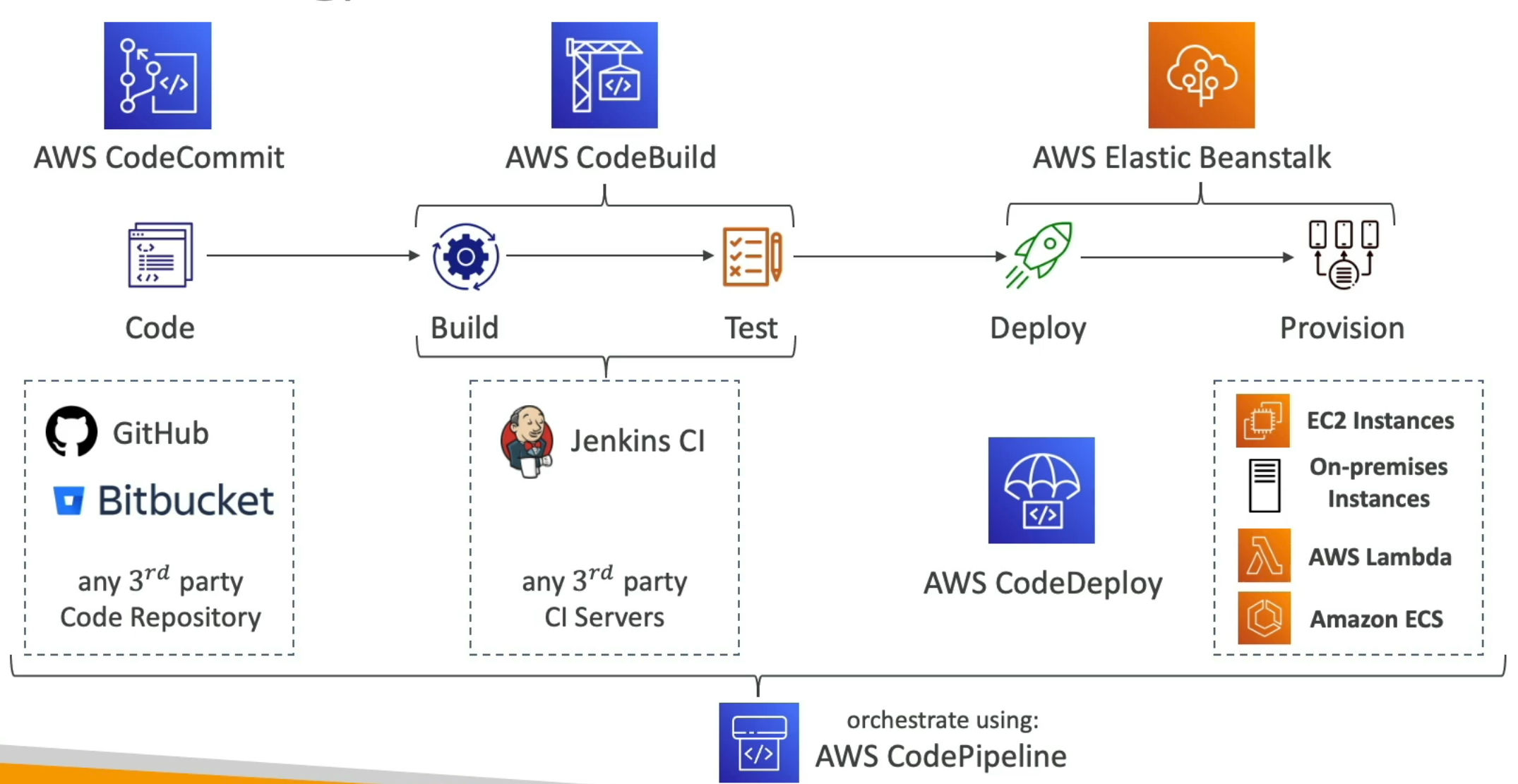
- Push our code to target repository and deploy automatically
- Make sure it's tested before being deployed
- With possibility to go into different stages (dev, test, staging, prod)
- With manual approval where needed
CI (Continuous Integration)
- Developers push the code to central code repository
- ex. Github, CodeCommit, BitBucket..
- A testing/build server checks the code as soon as it's pushed
- ex. CodeBuild, Jenkins CI ...
- Developer gets feedback about tests and checks that have passed / failed
- Find bugs early and fix bugs early
- Deliver faster as the code is tested
- Deploy often
- Developers are not blocked
CD (Continous Delivery)
- Ensures the software can be released reliably whenever needed
- Ensures deployments happen often and are quick
- Shift away from 'one release every 3 months' to '5 releases a day'!
- That usually means automated deployment
- ex. CodeDeploy, Jenkins CD, Spinnaker ...
CodeCommit
- Store our code
- Version Control
- Ability to understand the various changes that happened to the code over time (and possibly roll back)
- Enabled by using version control ssytem such as Git
- Git can be synchronized on your computer, but it usually is uploaded on a central online repository
- Benefits
- Collaborate with other developers
- Make sure the code is backed up somewhere
- Make sure it's fully viewable and auditable
- CodeCommit vs Github/GitLab/BitBucket
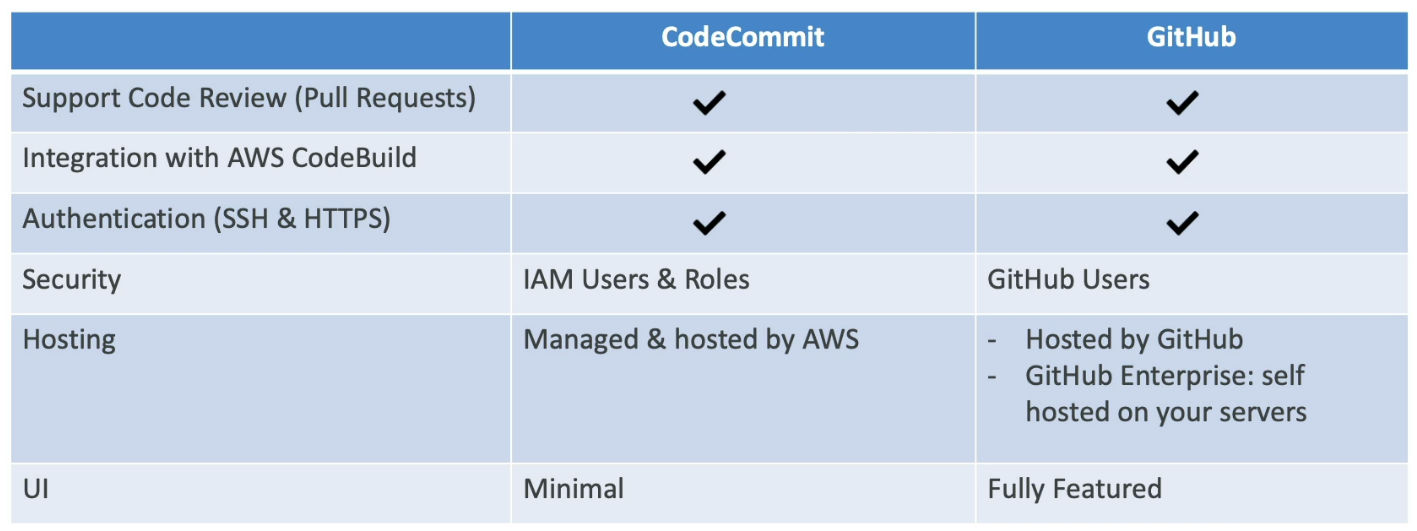
- Git repo can be expensive
- CodeCommit (From 2024.7.25 - discontinued => recommended to migrate to external Git solution)
- Private Git repositories
- No size limit on repositories (scale seamlessly)
- Fully managed, highly available
- Code only in AWS Cloud account => increased security and compliance
- Security (encrypted, access control ... )
- Interactions are done using Git
- Authentication
- SSH Keys - AWS users can configure SSH keys in their IAM Console
- HTTPS - with AWS CLI Credential helper / Git Credentials for IAM user
- Authorization
- IAM policies to manage users/roles permissions to repositories
- Encryption
- Automatically encrypted at rest using AWS KMS
- Encrypted in transit (can only use HTTPS or SSH - both secure)
- Cross-account Access
- Do not share your SSH keys or your AWS credentials
- Use IAM role in your AWS account and use AWS STS (AssumeRole API)
- Integrated with Jenkins, AWS CodeBuild, and other CI tools
- Monitoring with EventBridge
- In near real-time you can monitor CodeCommit events in EventBridge
- ex. pullRequestCreated, pullRequestStatusChanged, referenceCreated, commentOnCommitCreated ...
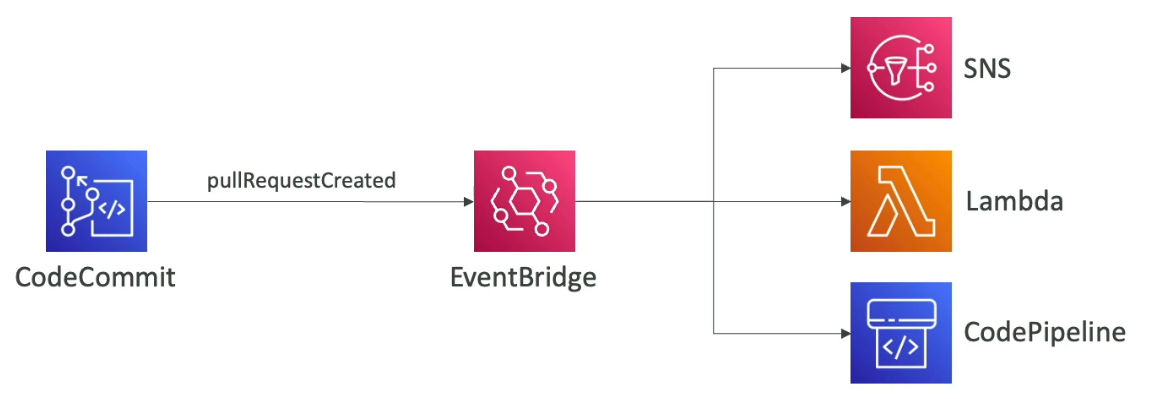
- In near real-time you can monitor CodeCommit events in EventBridge
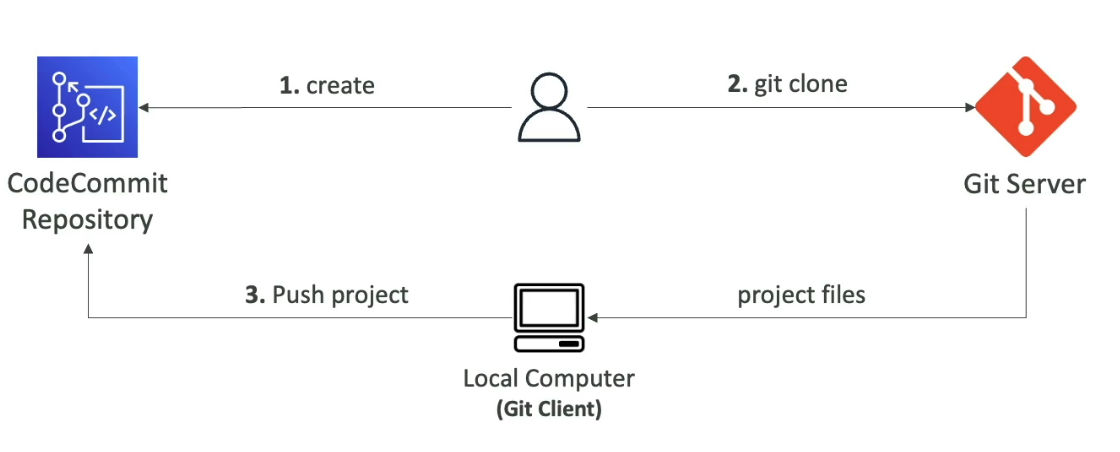
- How to migrate Git repository to CodeCommit
- You can migrate a project hosted on another Git repository to CodeCommit repository
- Cross-Region Replication
- ex. achieve lower latency pulls for global developers, backups ...
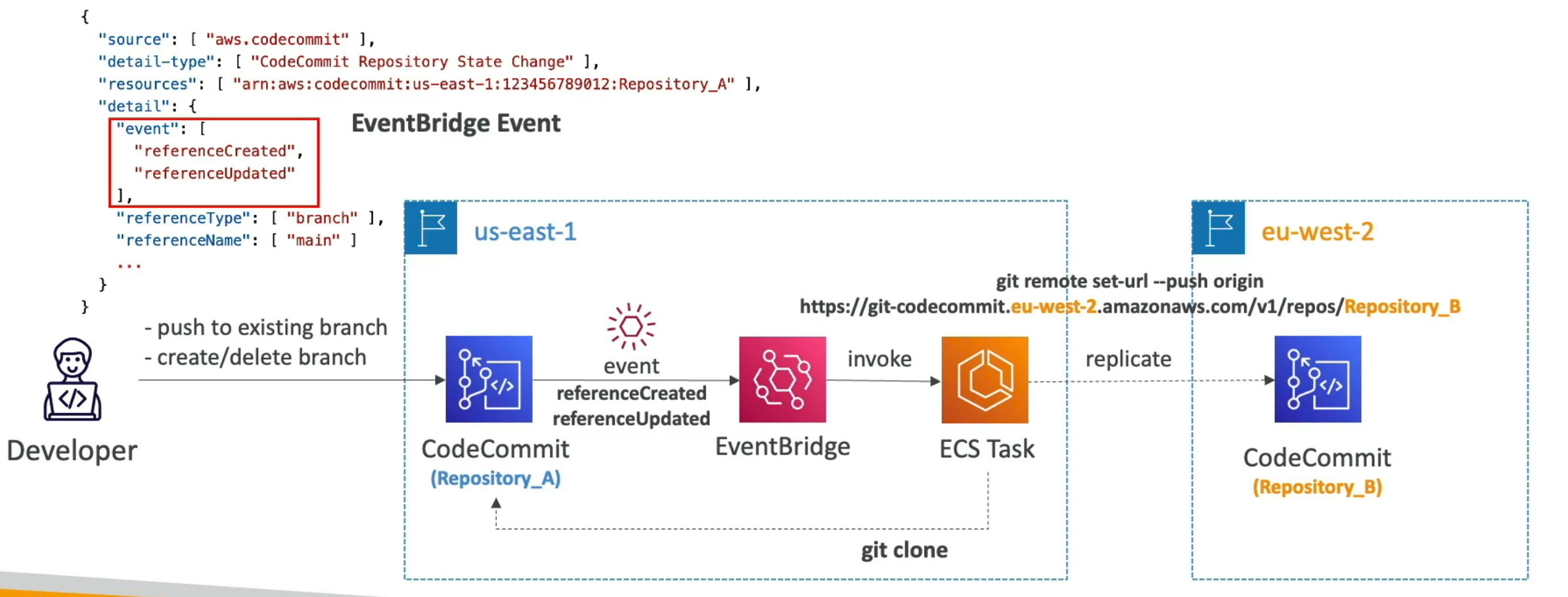
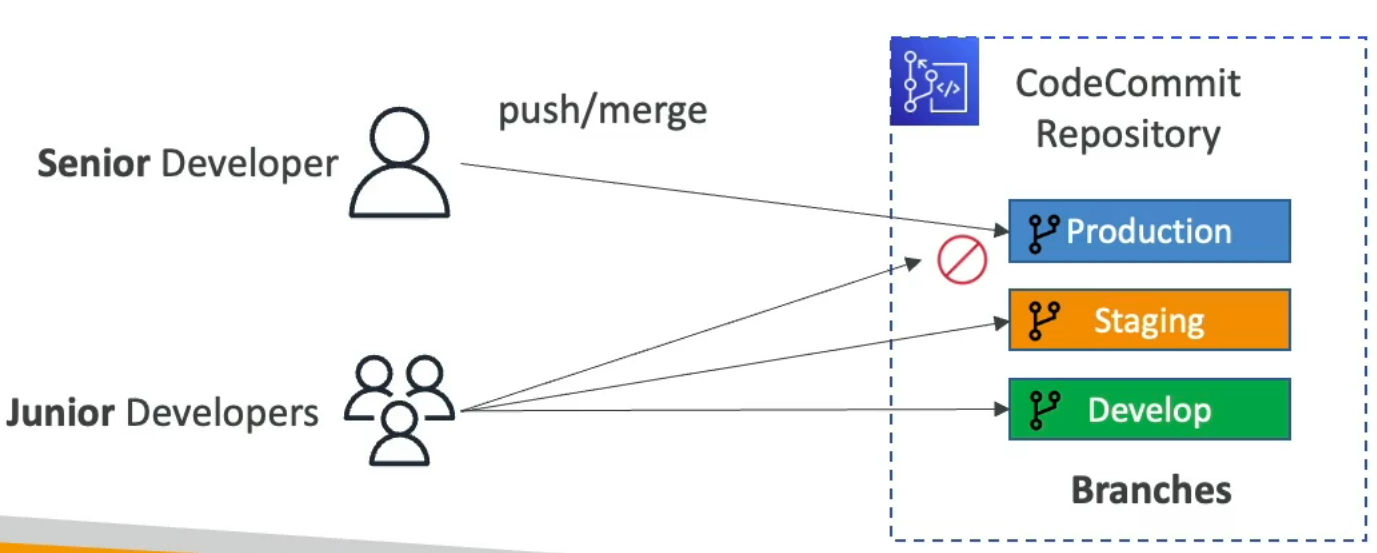
- Branch Security
- By default, a user who has push permissions to a CodeCommit repository can contribute to any branch
- To restrict to which branch they can contribute to, you need to use IAM policies for restricting users to push or merge code
- ex. only senior developers can push to production branch

- Resource Policies are not supported yet
- Pull request Approval Rules
- Helps ensure the quality of your code by requiring users to approve the open PRs before the code can be merged
- You need to specify a pool of users to approve and number of users who must approve the PR
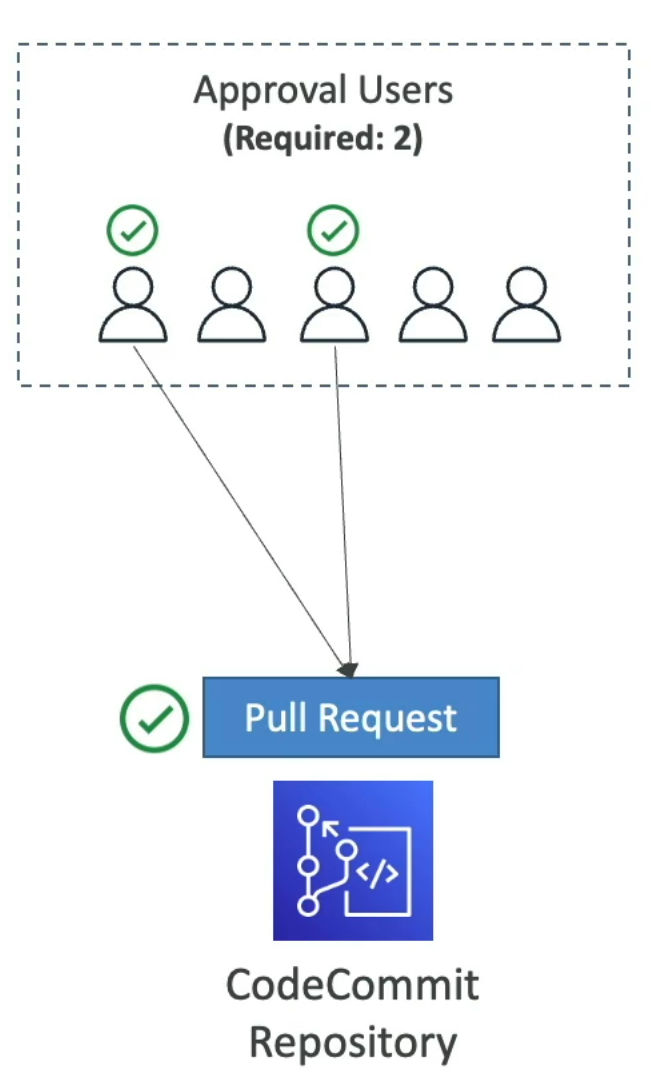
- Specify IAM Principal ARN (IAM users, federated users, IAM Roles, IAM Groups)
- Approval Rule Templates
- Automatically apply Approval Rules to PRs in specific repositories
- ex. define different rules for dev and prod branches
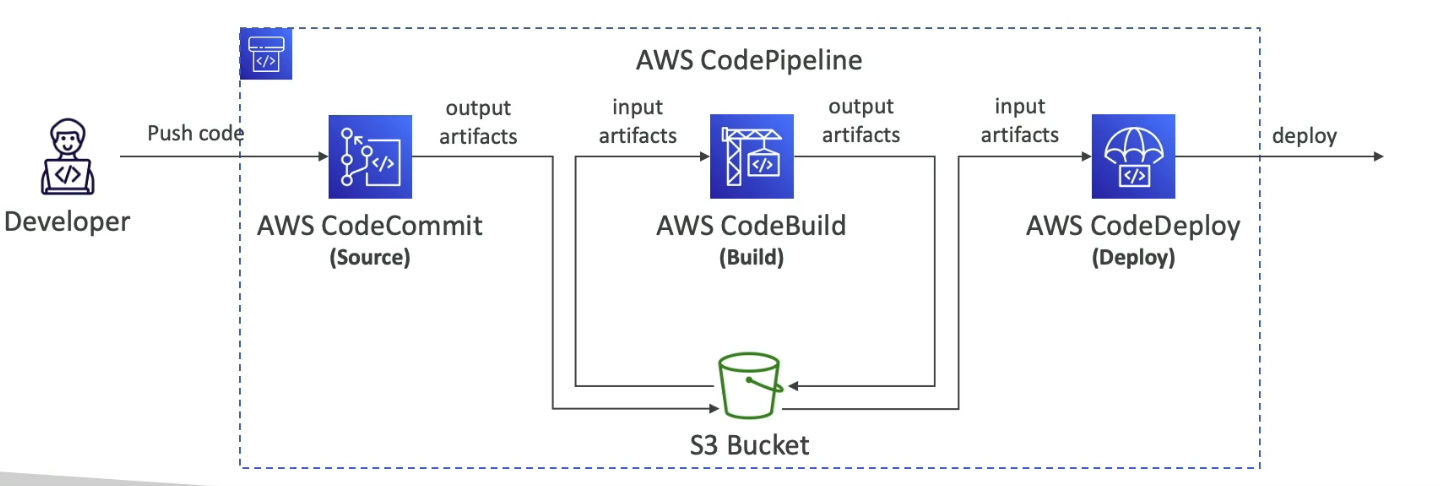
CodePipeline
- Automating our pipeline from code to Elastic Beanstalk
- Visual workflow to orchestrate your CICD
- Source - CodeCommit, ECR, S3, BitBucket, Github
- Build - CodeBuild, Jenkins, CloudBees, TeamCity
- Test - CodeBuild, AWS Device Farm, 3rd party tools ...
- Deploy - CodeDeploy, Elastic Beanstalk, CloudFormation, ECS, S3 ...
- Invoke - Lambda, Step Functions
- Build Stages
- Each stage can have sequential actions and/or parallel actions
- ex. Build => Test => Deploy => Load Testing (to make sure staging is doing fine) => deploy again...
- Manual approval can be defined at any stage
- How does it work?
- Each pipeline stage can create artifacts (Whatever created out of the pipeline)
- Artifacts stored in an S3 bucket and pased on to the next stage
- TroubleShooting
- For CodePipeline Pipeline/Action/Stage Executio State Changes
- Use CloudWatch Events (Amazon EventBridge)!
- ex. create events for failed pipelines
- ex. create events for cancelled pipelines
- If CodePipeline fails a stage, your pipeline stops, and you can get information in the console
- If pipeline can't perform an aciton, make sure the 'IAM Service Role' attached does have enough IAM permissions (IAM Policy)!
- AWS CloudTrail can be used to audit AWS API calls
CodeBuild
- Building and Testing our code
CodeDeploy
- Deploy the code to EC2 instances (not Elastic Beanstalk)
CodeStar
- Manage software development activities in one place
CodeArtifact
- store, publish, and share software packages
CodeGuru
- Automated code reviews using Machine Learning
Developing References
Developing Report
2025-01-17 - AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Professional Report
2025-01-17 - Developing Daily Report
2025-01-3th - Developing Weekly Report
